Warning
You are reading an old version of this documentation. If you want up-to-date information, please have a look at 1.1 .URCap global variables
The EYE+ URCap creates global variables dynamically to store some useful information. As soon as a URCap program node is opened with a connected EYE+, all global variables listed in the Table 3 are automatically created.
Name |
Description |
Type |
By default |
|---|---|---|---|
EYE1Prm |
Store the last EYE+ parameter after using get_parameter |
String |
“” |
EYE1AR |
Store the last Asycube response after using feeder |
String |
“” |
EYE1Pos |
Store the last EYE+ pick point position 1 read |
Position |
p[0,0,0,0,0,0] |
If the command set_parameter part_quantity n is used with n > 1, the global variables listed in Table 4 are automatically created (according to the value of n).
Warning
If the set_parameter part_quantity n command is sent using the URScript function, you must declare the global variable in Before Start yourself.
Name |
Description |
Type |
By default |
|---|---|---|---|
EYE1Pos2 |
Store the last EYE+ pick point position 2 read |
Position |
p[0,0,0,0,0,0] |
… |
… |
… |
|
EYE1Pos5 |
Store the last EYE+ pick point position 5 read |
Position |
p[0,0,0,0,0,0] |
EYE1Pos, EYE1Pos2, …, EYE1Pos5
These global variables store the last part coordinates received after sending a Basic command - get_part. The position variable is defined as: p[X,Y,Z,RX,RY,RZ] = p[X,Y,0,0,0,RZ].
The X and Y coordinates of the part stored in the variable are only valid in the robot frame that you defined during the hand-eye calibration. These coordinates are also only valid with the same Tool Center Point (TCP) as used during the hand-eye calibration.
Warning
For positioning the robot in space, the system uses meters.
The Z coordinate is set to 0. You have to add an offset in the Z direction to the TCP to avoid hitting the plate of the Asycube when picking up a part. (Installation/General/TCP).
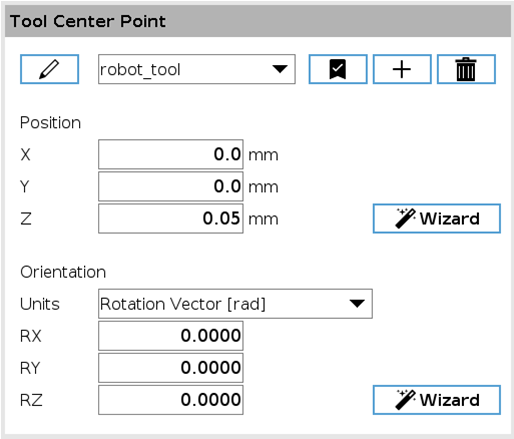
Fig. 23 Definition of the UR TCP with a Z offset of 0.05m.
The last 3 components of the position variable are set to [0, 0, RZ] where RZ is the angle sent by EYE+ in radian.
Warning
The global variable EYE1Pos is expressed in terms of roll, pitch and yaw. As the robot is expecting a rotation vector, you cannot directly move to the position. You at least have to add the 0-position of the robot as presented below.

Fig. 24 Position correction before Move
Most of the time, an RX or RY angle offset must be added to reach the part position.

Fig. 25 Position correction before Move with a correction on RX angle
To move the robot to the global variable coordinates, just select the basic robot command called Move. Make sure you use the right TCP and frame (Fig. 26) and then choose the type of move you want to perform (MoveJ, MoveL or MoveP). Finally, set the Waypoint equal to the global variable EYE1Pos. (Fig. 27).
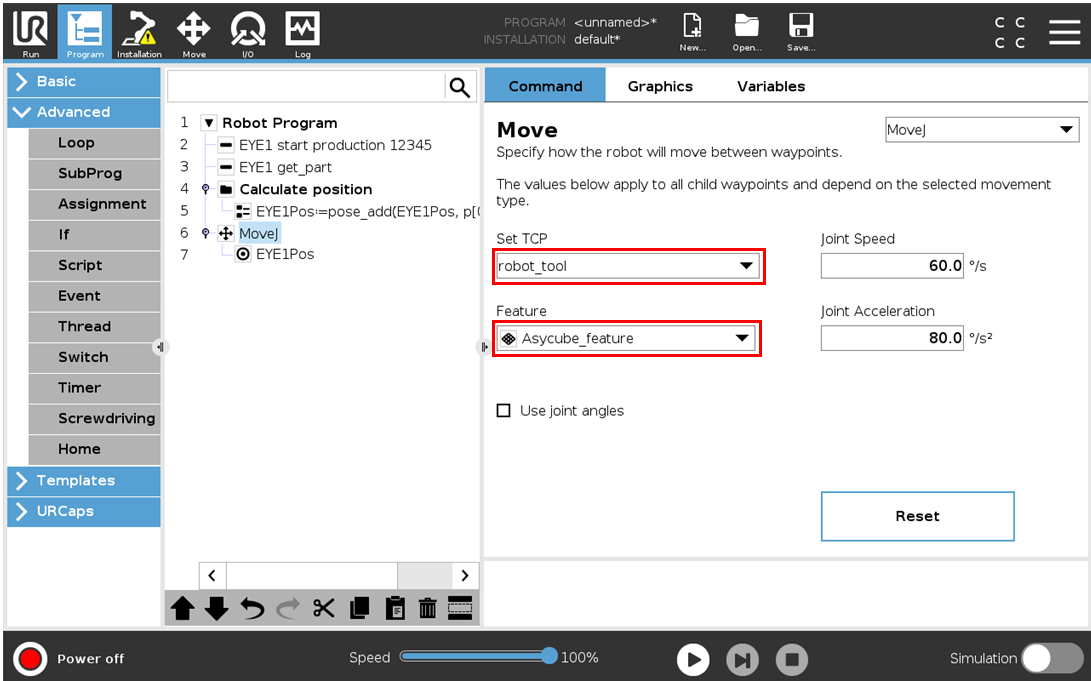
Fig. 26 Choose the right robot frame and TCP in the Move command
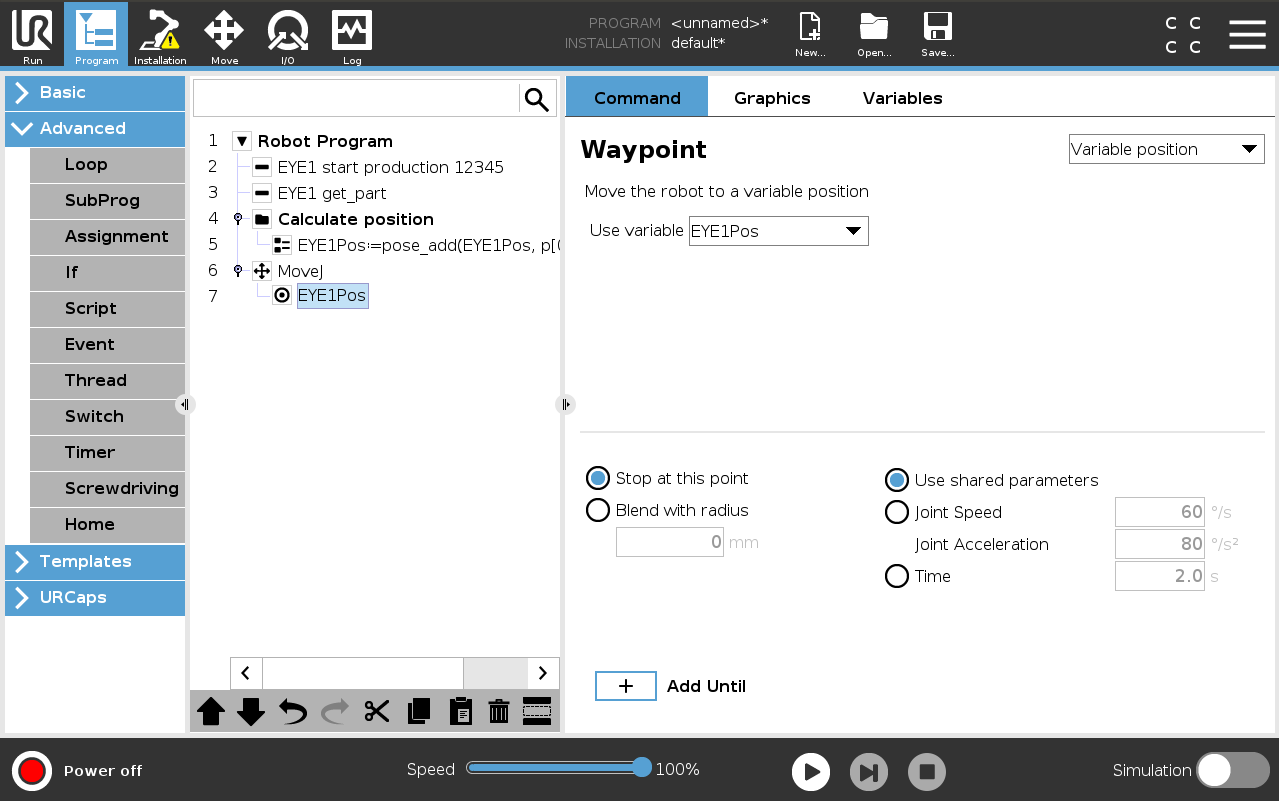
Fig. 27 Select the global variable EYE1Pos
EYE1Prm
This global variable is used to store the return value of the Advanced command - get_parameter command. Each time a new parameter is read, the last parameter stored in the variable is erased and replaced by the new one.
Important
If you run the get_parameter command using the URScript EYErawCommand(<name>, <command>) function, the EYE1Prm global variable will not be modified.
EYE1AR
This global variable is used to store the return value of the Advanced command - feeder command. Each time a new Asycube response is received, the last response stored in the variable is deleted and replaced by the new one.
Important
If you run the get_parameter command using the URScript EYErawCommand(<name>, <command>) function, the EYE1AR global variable will not be modified.