Plugin functions - URCap
You can start programming with the EYE+ plugin on the TeachPendant in the Program tab. The EYE+ URCap is called “EYE+ Control”. This URCap allows sending TCP/IP commands to the selected EYE+.
The connection between your EYE+ and your robot is established automatically before each TCP/IP command if it is not yet active.
Note
If the connection failed, the following error is displayed: 603 - Connection failed. If this is the case, check your configuration in the installation node.
Important
The camera configuration and hand-eye calibration must be done from the EYE+ Studio interface before executing any URCap commands. If you do not know how to proceed, please refer to the Camera configuration wizard and Hand-eye calibration wizard sections.
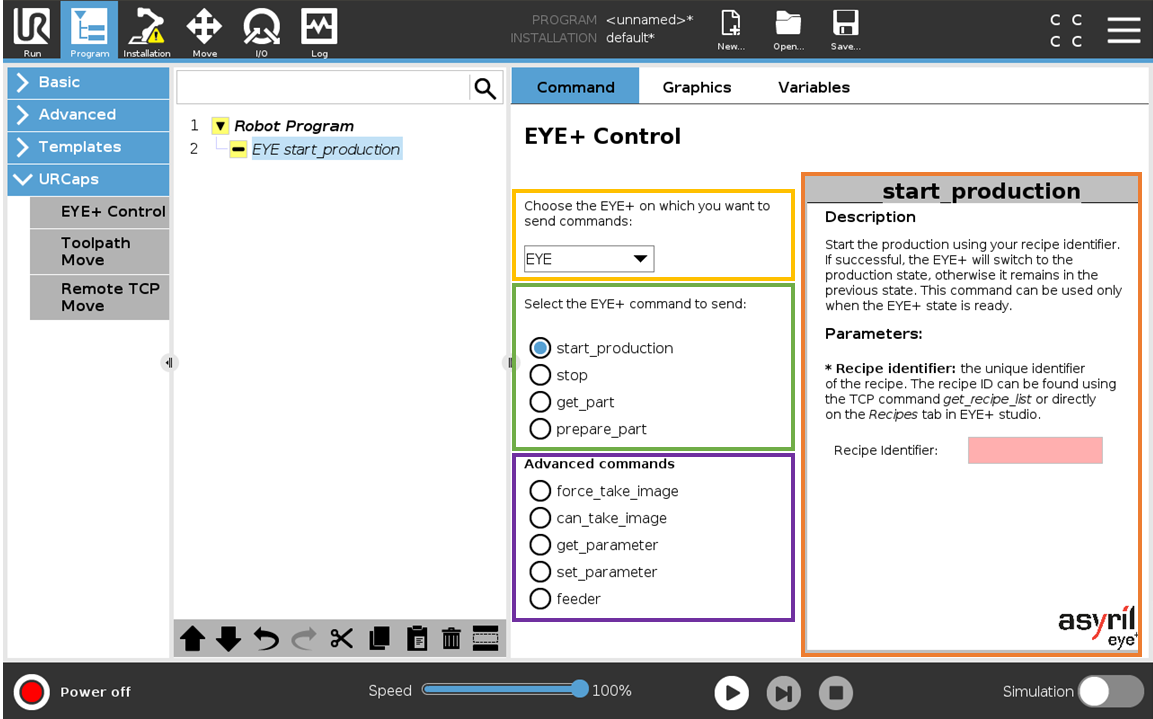
Fig. 7 EYE+ Control URCap - Advanced plugin selected
Select the EYE+ (yellow rectangle)
You must first select the EYE+ to which you want to send a command. All registered EYE+ are listed in the drop-down list.
Select a basic command (green rectangle)
Select the command you want to send to the EYE+. The basic commands available are start_production, stop, get_part, prepare_part. The view on the right (orange rectangle) changes depending on the selected command. This view gives some information about the behavior of the command in the Description field.
Note
Refer to chapter Commands for further information on the commands.
Select an advanced command (purple rectangle)
Select the command you want to send to the EYE+. The advanced commands available are force_take_image, can_take_image, get_parameter, set_parameter, feeder. The view on the right (orange rectangle) changes depending on the selected command. This view gives some information about the behavior of the command in the Description field.
Note
Refer to chapter Commands for further information on the commands.
Select parameter and argument (orange rectangle)
If the command requires input parameters or arguments, they must be provided in the right view.
Warning
If the parameter or argument is not valid according to the selected command, the node will not be defined (the node remains yellow and the main program cannot be started).
Basic commands
EYE start_production
The start_production command is the default command selected by the URCap. It is used to start EYE+ in the production state. This command requires the identifier of your recipe.
Note
The command will be invalid should the recipe identifier be left empty. The recipe identifier cannot be less than 0 and more than 65535.
Note
Refer to the section Recipes list if you do not know how to find the recipe identifier.
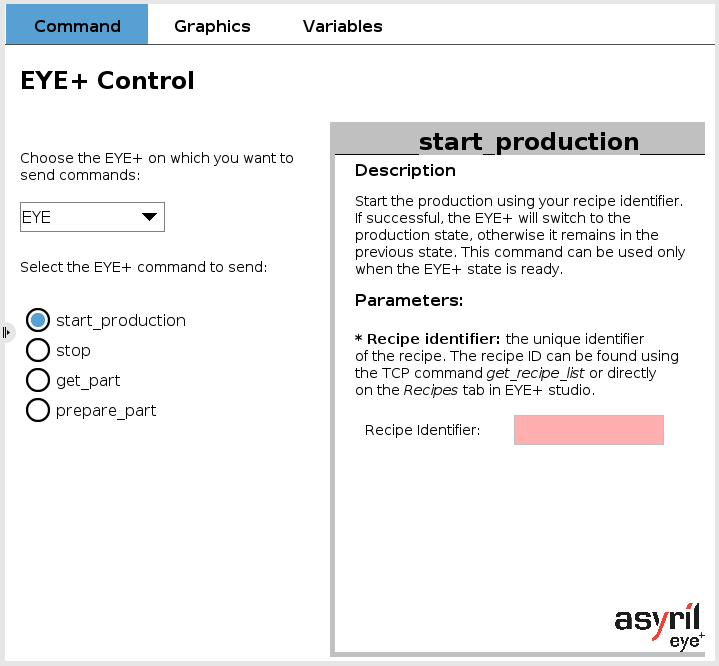
Fig. 8 EYE+ Control - start_production
EYE stop
The stop command is used to interrupt one of the EYE+ states. The state to be stopped can be chosen from the drop-down list. EYE+ switches to the ready state if the command succeeds.
This command is always valid if at least one EYE+ is connected.
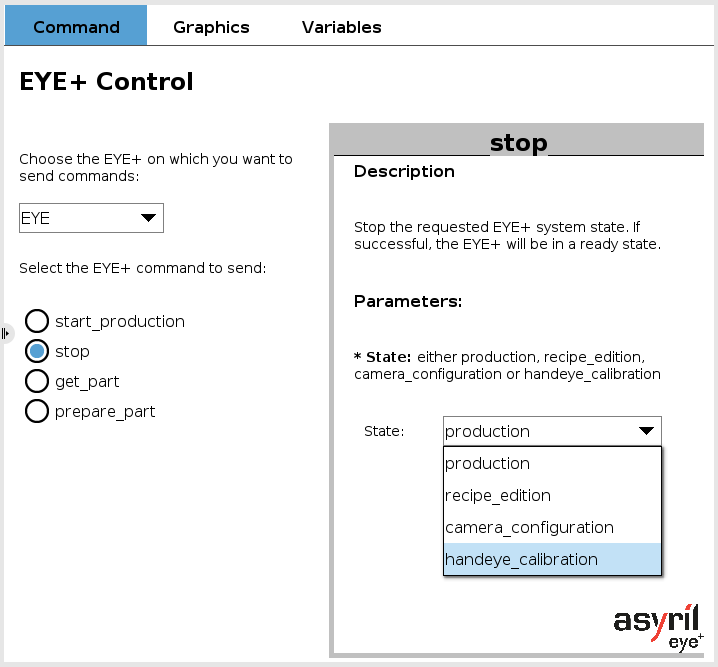
Fig. 9 EYE+ Control - stop
EYE get_part
The get_part command is used to request one or more parts from EYE+. This is a blocking command, meaning it will keep going until it gets a response from EYE+.
The coordinates of the first part returned by EYE+ are stored in a global variable named EYEPos.
Note
In advanced mode, if the part_quantity is set to more than 1, the next global variables are named from EYEPos2 to EYEPos5 according to the requested part quantity (using set_parameter part_quantity n command).
This command is always valid if at least one EYE+ is connected.
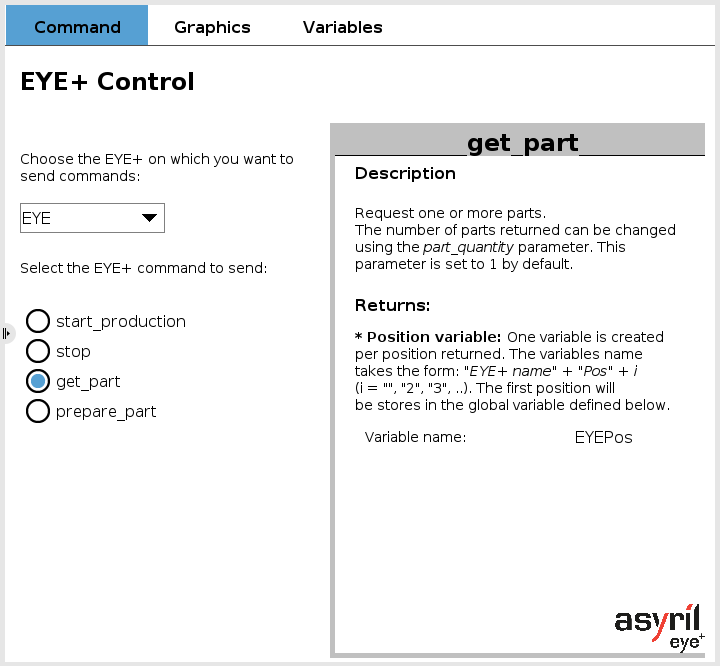
Fig. 10 EYE+ Control - get_part
Note
Refer to section EYEPos to get more information about the global variable EYEPos.
EYE prepare_part
The prepare_part command is used to request one or more parts from EYE+. This command is not a blocking command. The part coordinates can be retrieved later with the get_part command.
This command is always valid if at least one EYE+ is connected.
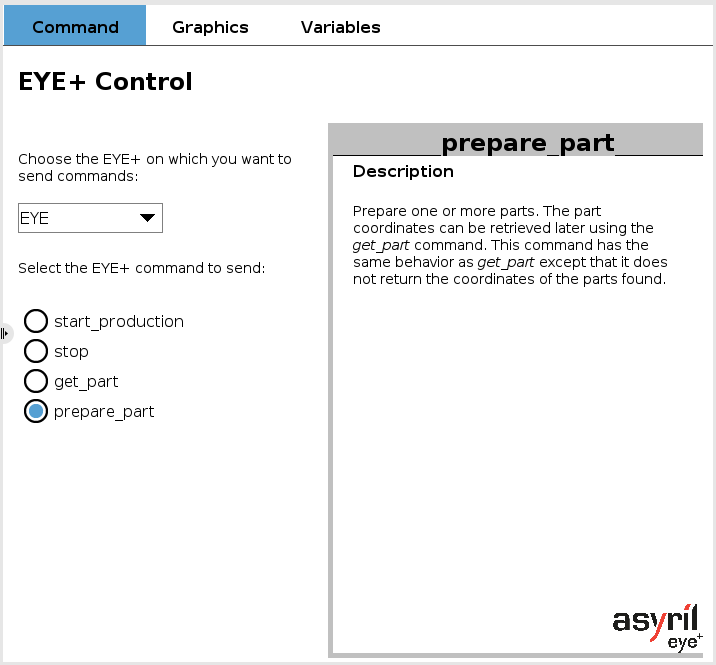
Fig. 11 EYE+ Control - prepare_part
Advanced commands
EYE force_take_image
This command forces EYE+ to acquire an image as soon as possible. Each time this command is called, an image is acquired and an image analysis is performed to find the coordinates of the good candidates.
This command is always valid if at least one EYE+ is connected and the advanced plugin mode is selected in configuration.
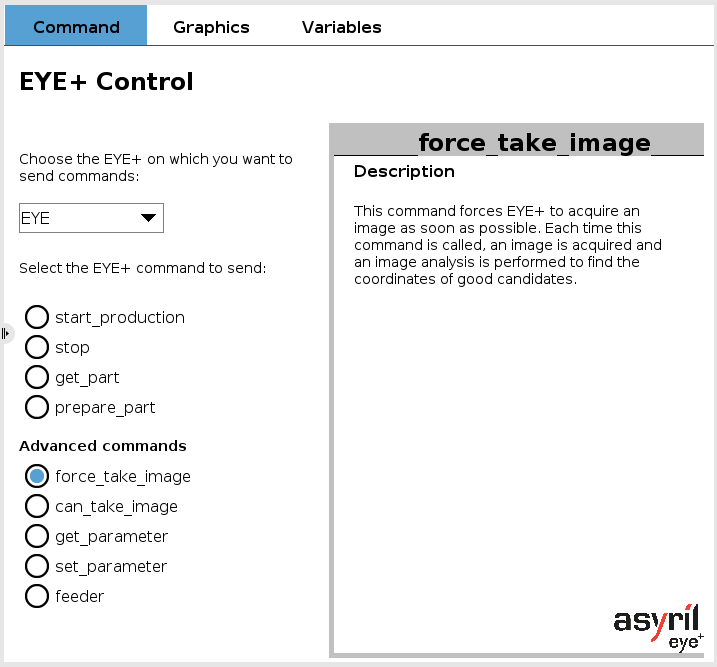
Fig. 12 EYE+ Control - force_take_image
EYE can_take_image
This command tells EYE+ whether it is allowed acquire an image. It requires a boolean input parameter.
If its value is set to True, EYE+ is allowed to acquire an image. It must be called when the field of view is clear of any object that could obstruct the image acquisition (for example, the robot).
If its value is set to False, EYE+ is not allowed to acquire an image. It must be used in the opposite situation of the one described above.
This command is always valid if at least one EYE+ is connected and the advanced plugin mode is selected in configuration.
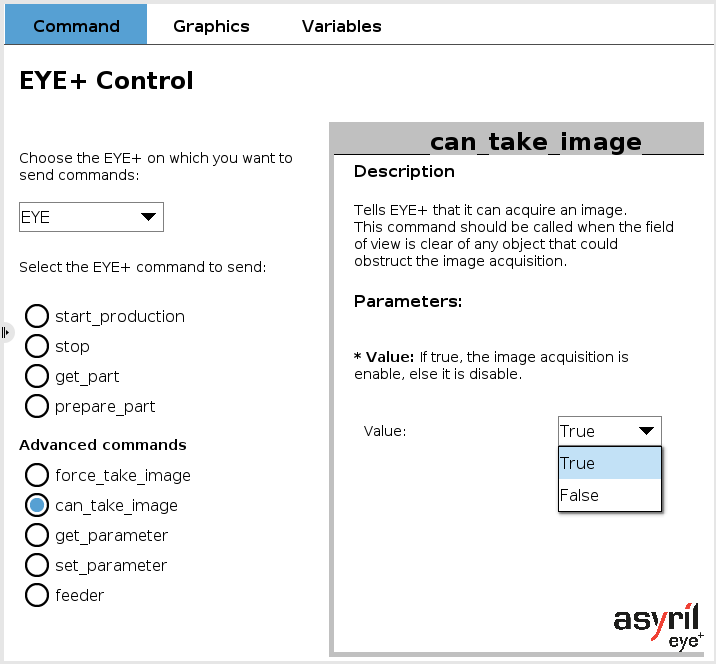
Fig. 13 EYE+ Control - can_take_image
EYE get_parameter
This command returns the value of the parameter specified as a command argument stored in EYE+. It requires a string as an input parameter. Refer to chapter List of parameters to check the valid parameters to get.
The returned value is stored in a global variable named EYEParam.
Important
If the input parameter does not exist, the command will return the error
404 The given parameter does not exist and the global variable keeps its former value. The error code can be
retrieved by calling the URScript function EYECheckLastError(<name = “EYE”>).
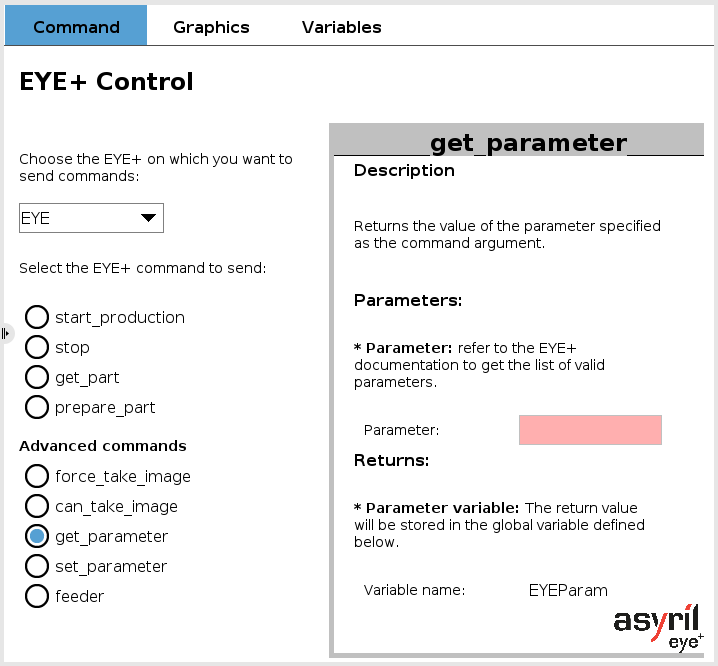
Fig. 14 EYE+ Control - get_parameter
Note
Refer to section EYEParam to get more information about the global variable EYEParam.
EYE set_parameter
This command assigns to the parameter of EYE+ a value equal to the argument of the command. It then requires an input parameter and an argument, both as strings. Refer to chapter List of parameters to check the valid parameters and arguments to set.
Important
If the input parameter does not exist, the command will return the error
404 The given parameter does not exist and the EYE+ parameter value will not changed. The error code can be
retrieved by calling the URScript function EYECheckLastError(<name = “EYE”>).
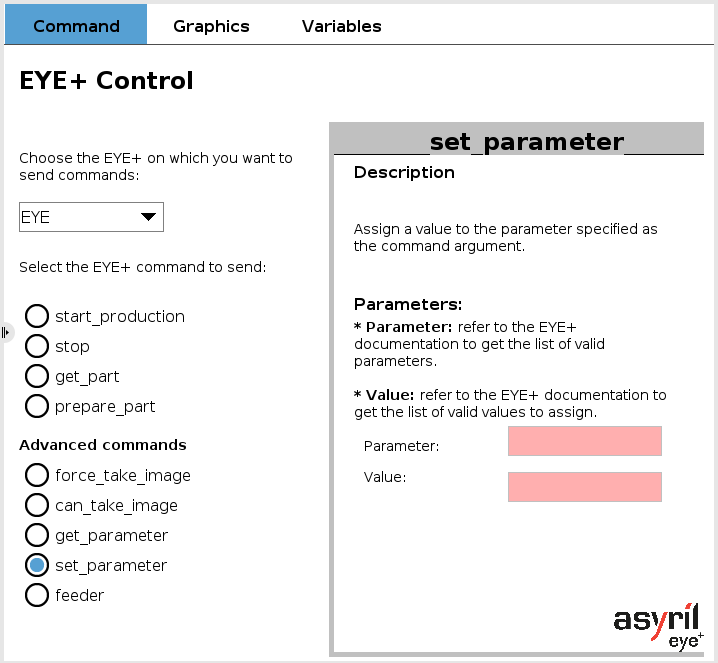
Fig. 15 EYE+ Control - set_parameter
EYE feeder
This command sends a raw Asycube command from EYE+ to the connected Asycube. It requires a string as a parameter.
The returned value is stored in a global variable named EYEAsyRes.
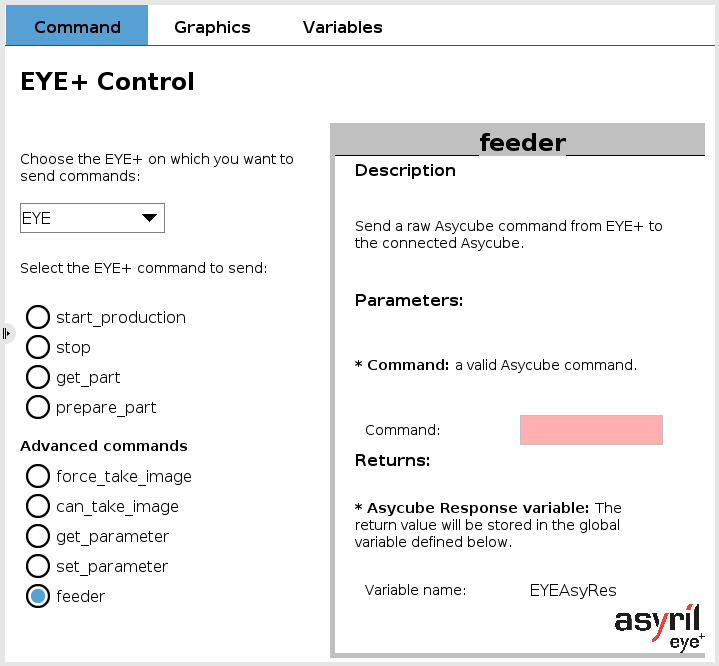
Fig. 16 EYE+ Control - feeder
Note
Refer to section EYEAsyRes to get more information about the global variable EYEAsyRes.