Warning
You are reading an old version of this documentation. If you want up-to-date information, please have a look at 5.2 .2.2 Filter isolated parts
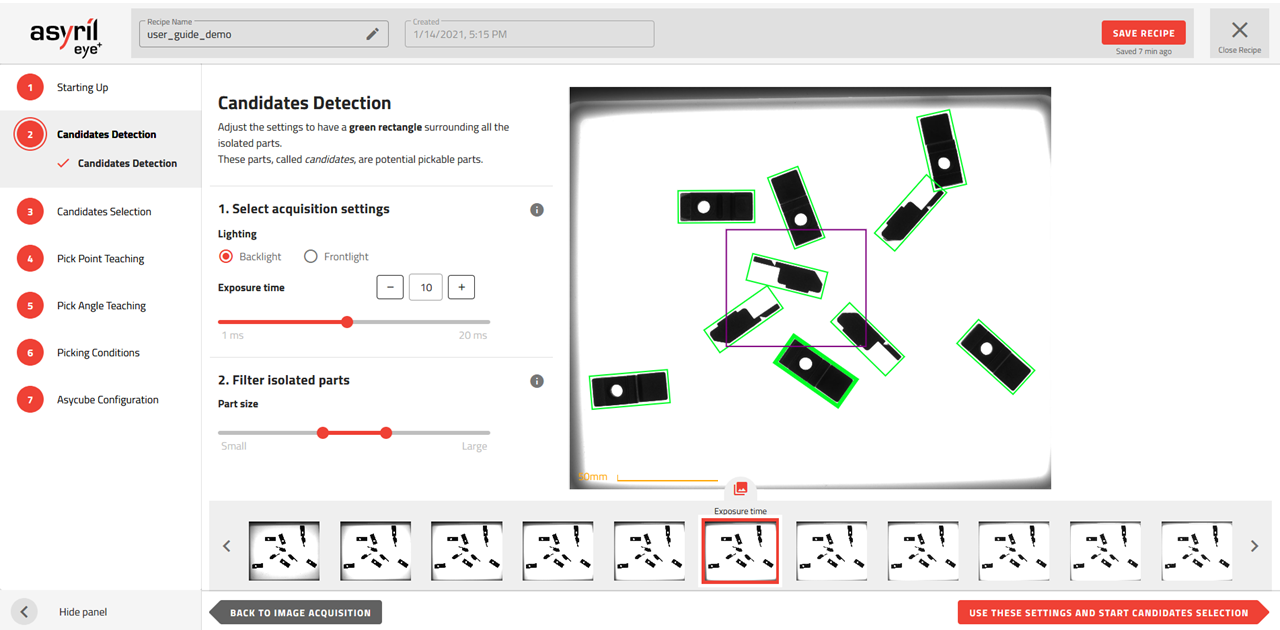
Fig. 53 Candidate Detection - Filter isolated parts
All contours detected by the algorithm can now be filtered depending on their size. The size of a part is defined by the surface
area of the box enclosing the detected element. You can define which surface (i.e. part size) is considered as good by adjusting
the double slider  . You must define a minimum and maximum detection size. All contours within this minimum and maximum
surface area will be detected as a part and thus considered as a candidate for the next steps
. You must define a minimum and maximum detection size. All contours within this minimum and maximum
surface area will be detected as a part and thus considered as a candidate for the next steps
Important
If a part is not surrounded by a green rectangle at the end of this step, note that it will be discarded for all the following steps, meaning that it will not be picked by the robot before a vibration is made to change its position or orientation.
Note
The algorithm is looking for a closed border. When a closed border is detected, the algorithm calculates the minimum rectangle that can surround this border. If the surface of the bounding box is within the defined range, it will be displayed on the image as a green rectangle surrounding the detected elements.
Note
If the part is a bit outside the Region of Interest (ROI), the detected borders of the part are cut as shown in Fig. 54. The bounding boxes may have a different size because of this. This part can still be used for the next steps but you should be aware that from the system point of view, the part is cut on the side.
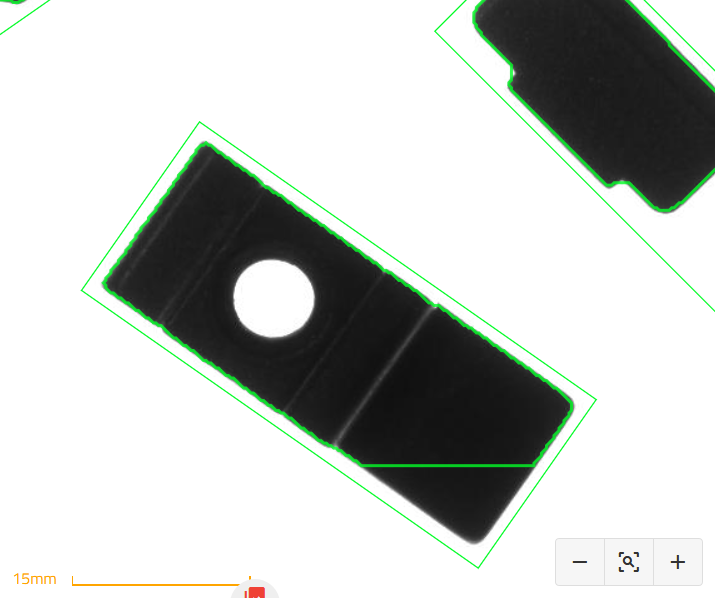
Fig. 54 The part is cut because it is a bit outside the ROI
Range of sizes is too low or too high
Too low: Risk of detecting small dirt or shadows.
Too high: Risk of detecting a group of parts as a single part.
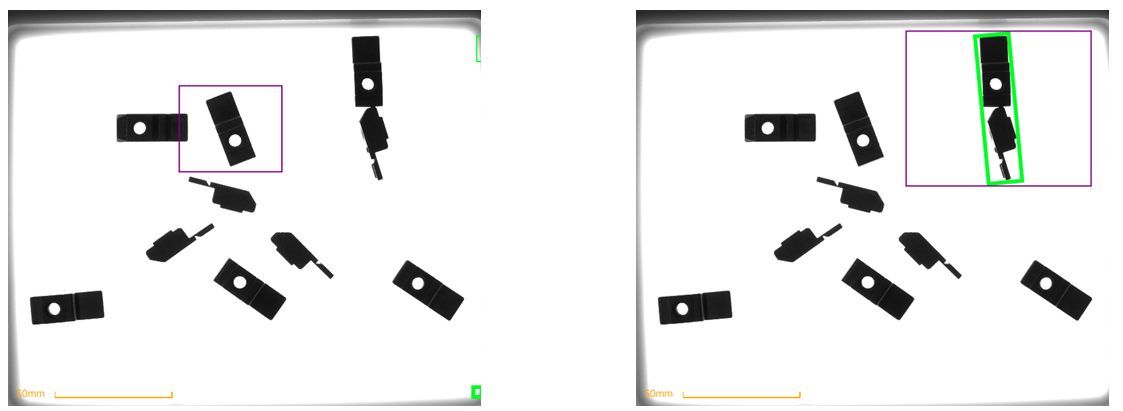
Fig. 55 Range of sizes: too low (left), too high (right) [Backlight - 13ms]
Range of size too narrow or too large
Too narrow: Part detection may not be robust enough to detect a part in different positions in the image (slight change in the surface of the part seen by the camera). The risk is to reject a part only because its surface is slightly out of the desired range.
Too large: Risk of detecting too many different part sizes and detecting groups of parts as a single part.
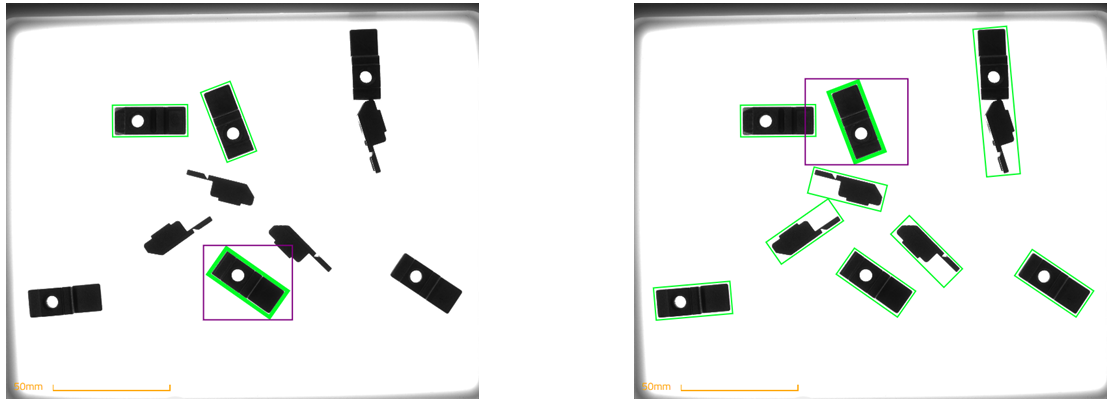
Fig. 56 Range of sizes is too narrow (left) or too large (right) [Backlight - 13ms]